Laying a Strong Foundation for Buildings
Just like a tree needs its roots to be strong and deeply entrenched in the soil, a building also needs a strong foundation to stand on. There are two types of foundations for building construction – shallow and deep. It is advisable to know the properties of each type of foundation before using them in any construction project.
Types of Foundations and Selection Criteria
Shallow and deep foundations can be further divided into the following categories:
Types of Shallow Foundations
Individual footing or isolated footing –
This foundation is constructed for a single column and is the most common type of
foundation used for building construction. An individual footing is square or rectangular and is used when the columns carry the load of the structure. The foundation’s size is calculated based on the load on the column and safe bearing capacity of the soil. Rectangular isolated footing is selected when the foundation is subject to eccentricity of loads or horizontal forces.
Combined footing –
Combined footing is rectangular in shape and is used when two or more columns are close enough and their isolated footings overlap each other. It is a combination of isolated footings, but their structural design differs.
Spread footings or strip footings and wall footings –
Spread footings have a wider base compared to typical load-bearing wall foundations. This spreads the weight from the building structure over more area and provides better stability. Spread footings and wall footings are used for individual columns, walls and bridge piers where the bearing soil layer is within 3 m (10 feet) from the ground surface.
Raft or mat foundations –
These foundations are spread across the entire area of the building to support heavy and high structural loads from columns and walls. A mat foundation is used to prevent differential settlement of individual footings. It is therefore designed as a single mat (or combined footing) of all the load-bearing elements of the structure. Raft foundation is economical when one-half area of the structure is covered with individual footings and wall footings are provided.
Types of Deep Foundations
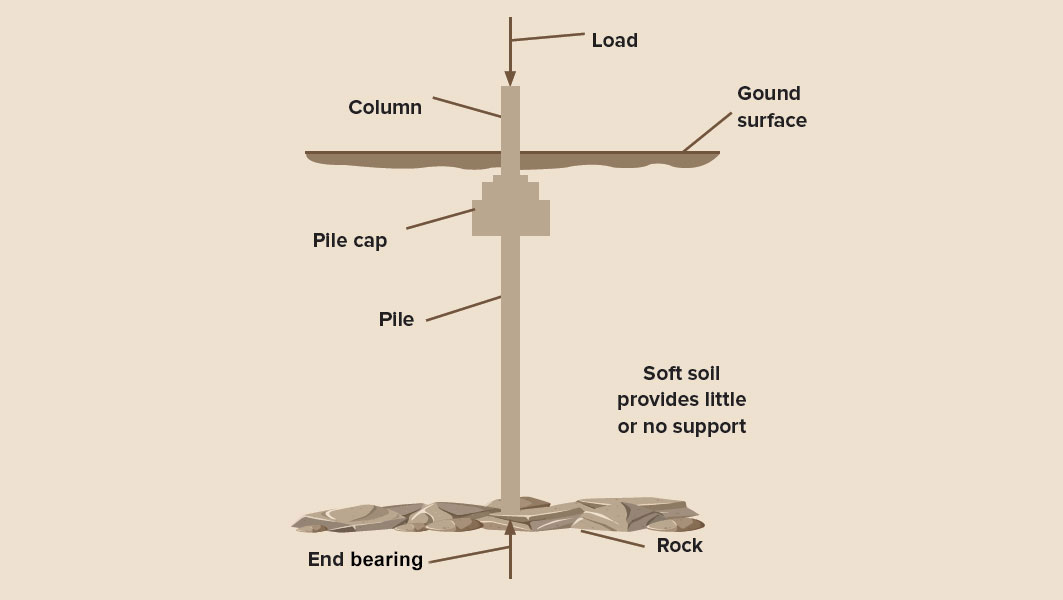
Pile foundations –
Pile foundation is a type of deep foundation used to transfer heavy loads from the structure to a hard rock strata much deep below the ground level where shallow foundations such as spread footings and mat footings cannot be used. It is also used to prevent the building from being uplifted by earthquakes and wind forces. A pile foundation resists the loads from the structure by skin friction and end bearing. It also prevents differential settlement of foundations.
Drilled shafts or caisson foundation –
A drilled shaft, also called a caissons, plays a role similar to that of a pile foundation, but is a high-capacity castin- situ foundation. It fights loads from the structure through shaft resistance, toe resistance and/or a combination of both. The construction of drilled shafts or caissons are done using an auger. Drilled shafts can transfer column loads larger than pile foundations.



